This article will help you to organize accounting for the company, whose use a production process.
Production - is the transformation of objects into the other with the use of labor. Consider the scheme of an enterprise engaged in production.
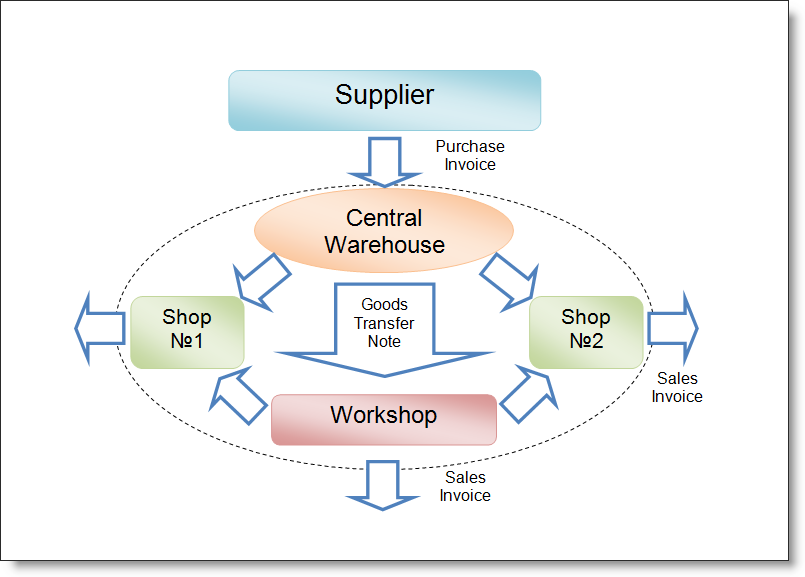
The production activities can be divided into several stages, and reflect this in the next document sequence:
- Arrival of the goods (ingredients) from supplier reflects in Purchase Invoice.
- Transfer ingredients from a warehouse to the worksop reflects in Transfer Order.
- Production as conversion ingredients into the products reflects in Productionl Act.
- Transfer to the finished goods warehouse reflects in Transfer Order.
- Product sales (wholesale and retail) can be reflect in Sales Invoice.
For production accounting will be convenient to create separated location (workshop) in the Locations Dictionary. It must be noted that that receipts and expenditures of the goods can be carried out directly on the production workshop. But even if, in reality, production and sales occur in the same place (eg cafe with kitchen), we recommends to create separate location (workshop) for the production processes implementation. This will give us more control in accounting, visibility and convenience it to analysing.
Let us consider the production process example.
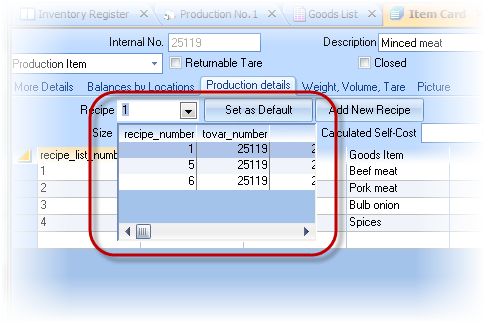
There is a company which manufactures frozen food (dumplings, etc.). On the agenda - the introduction of a new product "Dumplings (weighted) with pork/beef. According by the technology to produce 100 kg dumplings we should take 50kg of minced meat and 50kg of dough (all data are not precise formulations, and are taken only for clarity). However, minced meat and the dough is not raw ingredients, we also have the recipes for them. Therefore we introduce new two products in the Goods Dictionary (you can create a separate Goods Category for them, such as "Semiproducts"): "Minced pork / beef" and "Dough". Do not forget to set the type of them as a product. In the Goods Item Card open the tab "Production Details" and enter the data for the recipe.
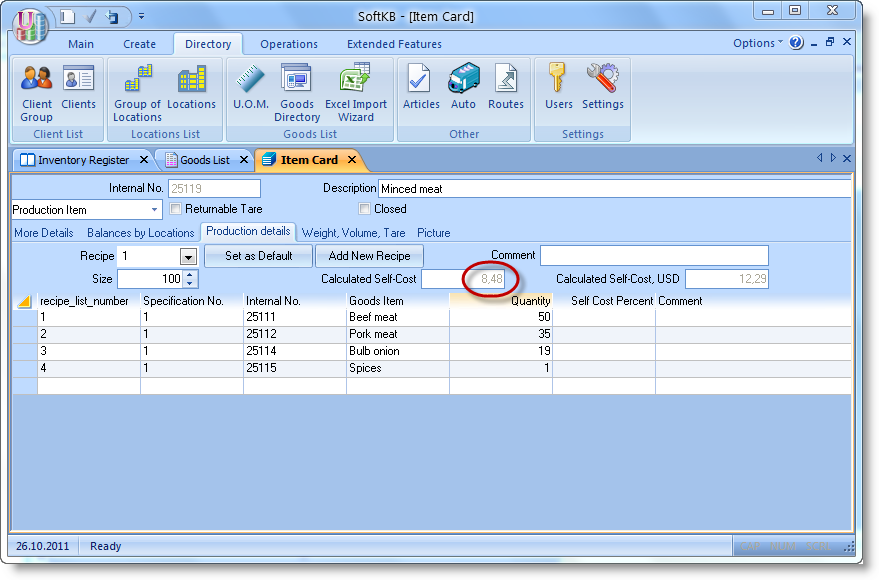
Note the field "Calculated self-cost". By the adding ingredients into the recipe and set the quantity of them value of this field will be change. As a result, we obtain the calculated self-cost per unit of product. Now we can set the retail price in the Goods Dictionary based on this self-cost. Retail price can be changed in future by the Revaluation Act if will need it.
Now in the Goods Dctionary, create a new item "Meet Dumplins", all actions similar to those described above:
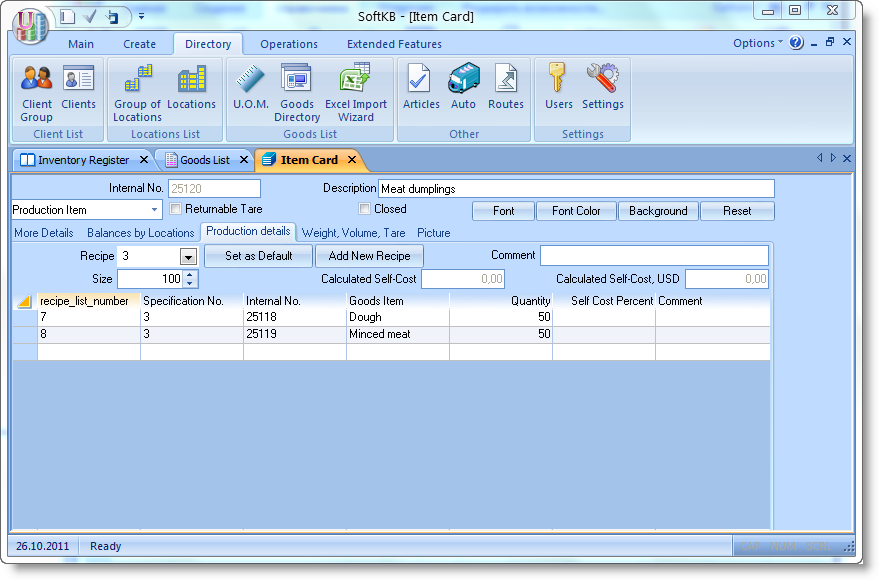
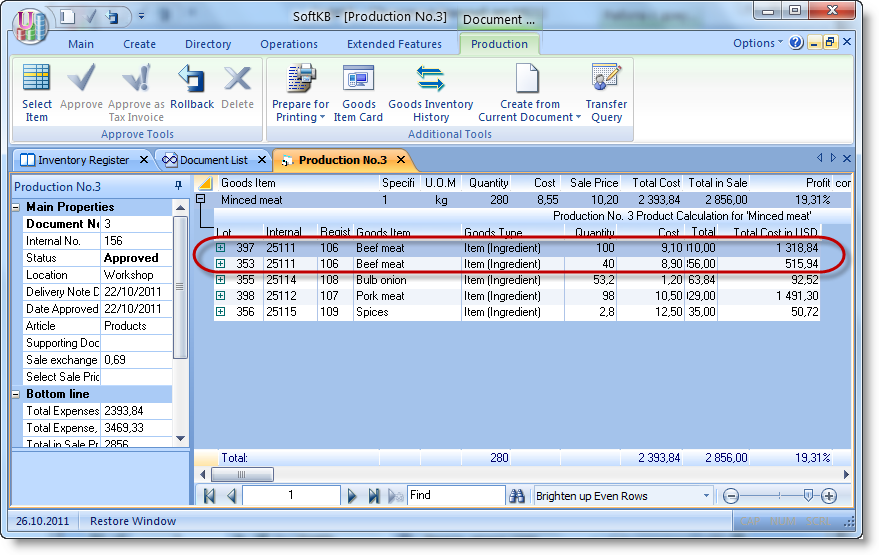
Let today we produced 50kg of dumplings. Create a new document "Production Act" and approve it.
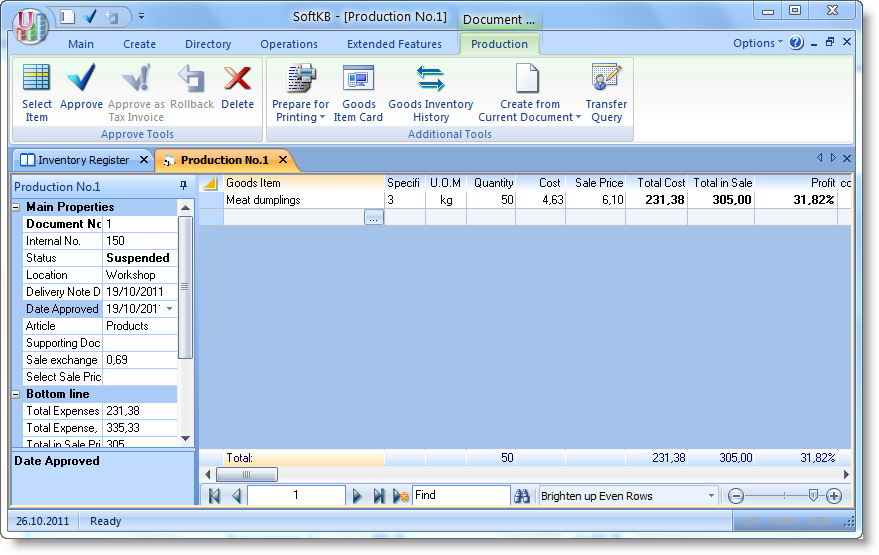
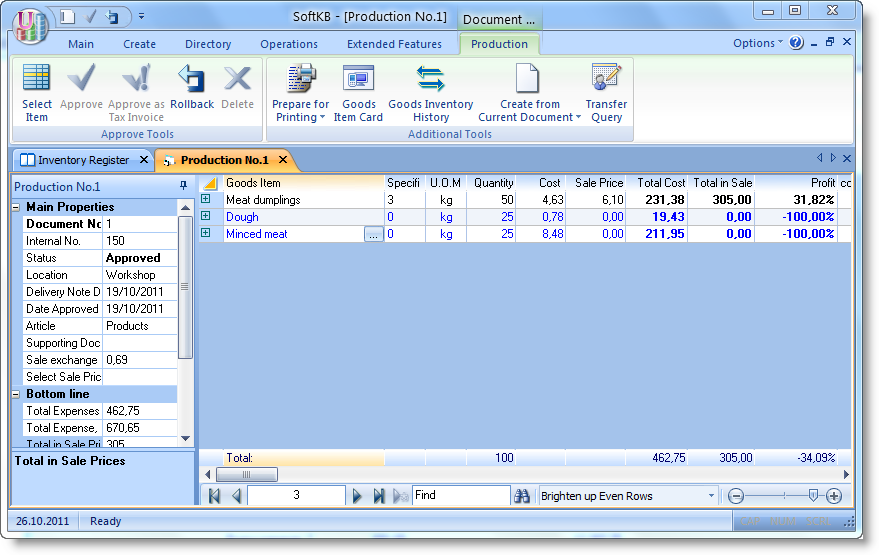
We can see, that the new positions which highlighted in blue was appeared. But we not entered them. The TCU automatically produces needed quantity of semiproducts (minced meat and dough).
During the approving of the document, there is an automatic consumption in needed quantity of ingredients, and the creating of the manufactured products. If we click "plus" in the beginning of the line, we can see the calculation card of the product. Here you can see which ingredients and semiproducts in what quantities and at what price had been spent for the production of our 50kg of the dumplings..
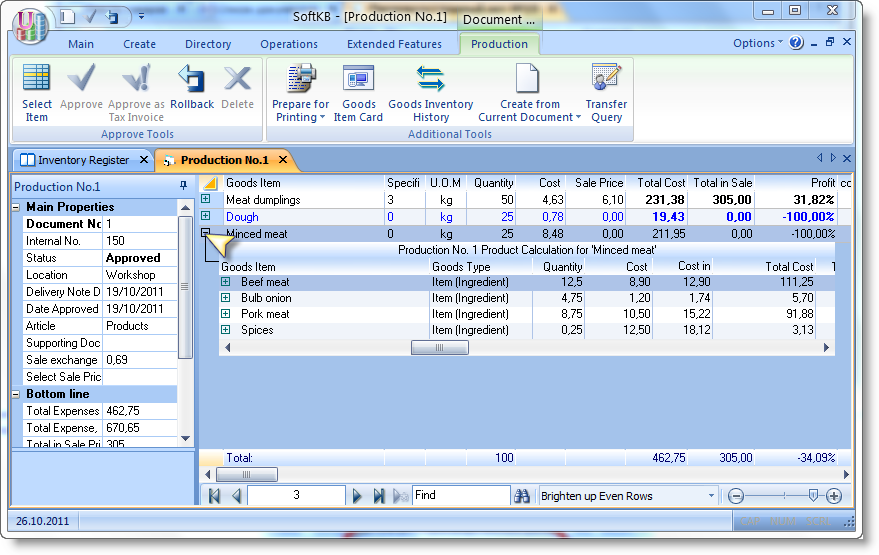
Note that for one product may be a few recipes that are made to the card product. Each recipe have assigned number. When you create new Production Act you can specify the number of required recipe, and TCU will produce the product at the specified recipe.
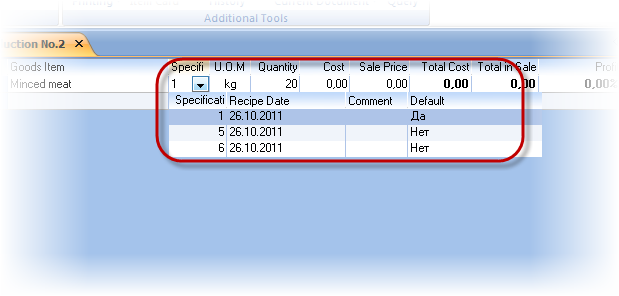
May be a situation when you need to produce a greater number of semi-finished products than is required for the final product. For example, apart from dumplings to 50kg 30kg to produce more meat for sale. In this case, simply add to the production act this product, and the system will do for him calculation separately.

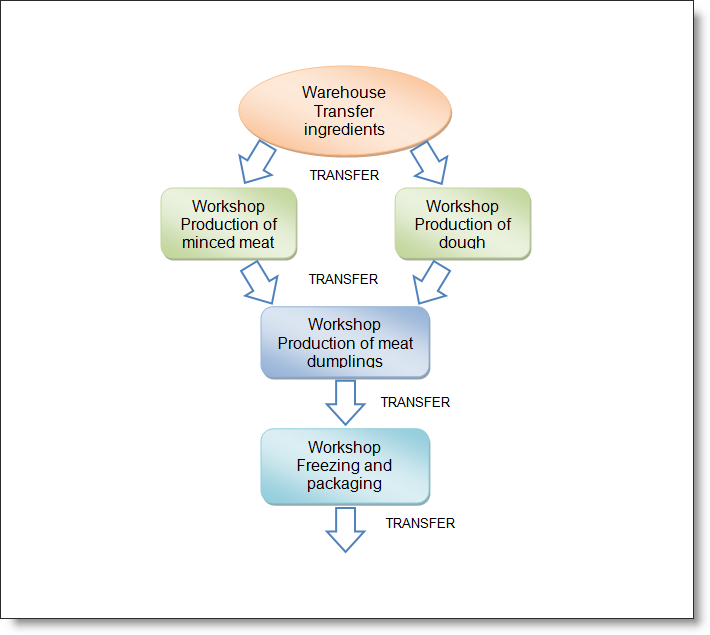
In principle, the stages of production can be as long as necessary. Suppose now we want to freeze and packed our dumplings. Create a new item "Dumplings packed 1kg" and make new production recipe - at 100kg of frozen packaged raw meat dumplings will need to 95kg (5kg for freezing) and 60 meter packing tape.
Consider the case when we produce minced meat in one place, dumplings produced in second workhop, pack in the third. Nothing complicated. Add workshops into the Locations Dictionary and produce and transfer semi-finished products from one shop to another.
And, finally, a few notes:
1. In TCU self-cost calculation is based on the FIFO mechanism (first in - first out). First spent parties, which came first. However, different parties may have different product purchase price. The TCU reads the purchase price for an ingredient in the time of consumption for producing, and automatically generates the cost of the product. If a product is taken from different parties with different purchase prices, it well be displayed in the act of production ("+", "Costing products »).
2. In the recipe the proportions of ingredients best not to specify for a single unit of product. The higher value in the "size", will be give more accurate calculation.
3. The results of calculation of any Production Act can be obtained more clearly in the Report Wizard, Report "Calculation Cards."
Note: This article was obtained through a machine translation. We would appreciate any comments.